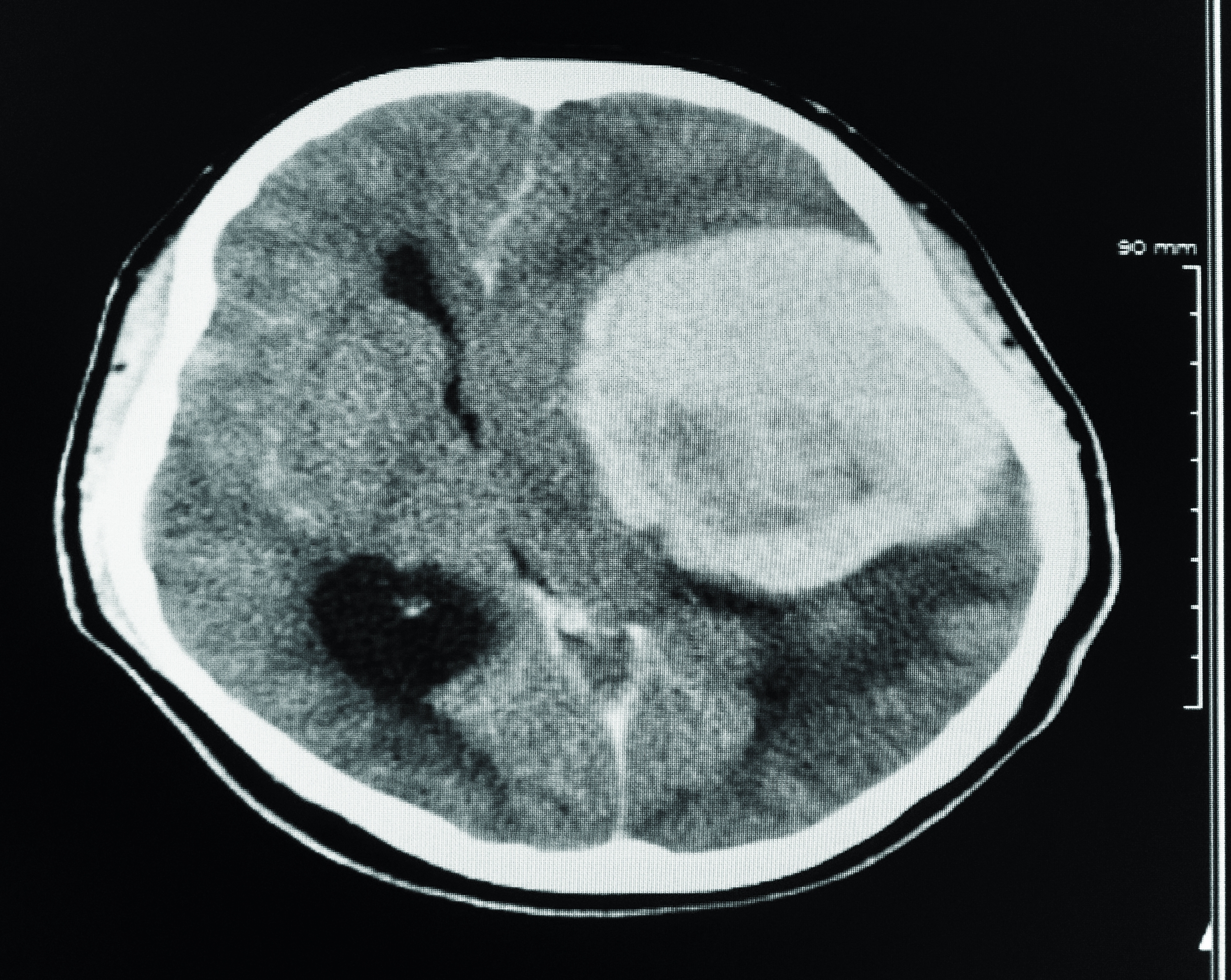
When you think of an eye doctor, you probably imagine someone checking your vision or prescribing glasses. But did you know that an eye doctor might also play a critical role in detecting serious health conditions, like brain tumors? The eyes are often referred to as the "windows to the soul," but they can also serve as windows to the brain. During routine eye exams, optometrists and ophthalmologists can observe subtle changes in the eyes that may indicate underlying neurological issues. These changes can sometimes point to the presence of a brain tumor, making early detection possible before symptoms become severe.
While brain tumors are relatively rare, their symptoms can mimic other less serious conditions, such as migraines or vision problems. This is why understanding the connection between eye health and brain health is crucial. Eye doctors are trained to spot abnormalities such as optic disc swelling, double vision, or unexplained vision loss, all of which could be linked to a brain tumor. By recognizing these signs early, they can refer patients to neurologists or other specialists for further evaluation, potentially saving lives.
In this article, we will explore the fascinating relationship between eye health and brain tumors, diving into how eye doctors can identify warning signs, what symptoms to look out for, and what steps to take if a problem is suspected. Whether you’re curious about how routine eye exams can uncover hidden health issues or seeking peace of mind about your vision and brain health, this guide has you covered. So, let’s dive in and uncover the answers to the question: Can an eye doctor detect a brain tumor?
Read also:Vega Movies 18 A Comprehensive Guide To Adult Cinema And Entertainment
Table of Contents
- How Can Eye Exams Detect Brain Tumors?
- What Are the Signs of Brain Tumors in the Eyes?
- Can an Eye Doctor Detect a Brain Tumor?
- How Do Brain Tumors Affect Vision?
- What Should You Do If a Problem Is Suspected?
- Why Are Regular Eye Exams Important for Brain Health?
- What Are the Limits of Eye Doctors in Brain Tumor Detection?
- Frequently Asked Questions
How Can Eye Exams Detect Brain Tumors?
Eye exams are not just about checking how well you can see. They involve a comprehensive evaluation of the eyes, including the retina, optic nerve, and blood vessels. During these exams, eye doctors use specialized tools to examine the back of the eye, where the optic nerve connects the eye to the brain. This connection is crucial because any pressure or damage to the brain can affect the optic nerve, leading to visible changes during an eye exam.
One of the most common signs that an eye doctor might notice is optic disc swelling, also known as papilledema. This condition occurs when there is increased pressure in the brain, often caused by a tumor pressing on the brain tissue or obstructing cerebrospinal fluid flow. Papilledema is a red flag that prompts further investigation, as it is not something that occurs in isolation without an underlying cause.
In addition to papilledema, other signs such as irregular eye movements, unexplained double vision, or sudden vision loss can also raise suspicions. These symptoms are not always obvious to the patient, especially if they develop gradually. However, an experienced eye doctor can detect these subtle changes and recommend additional tests, such as an MRI or CT scan, to determine the root cause.
What Are the Signs of Brain Tumors in the Eyes?
Brain tumors can manifest in a variety of ways, and the eyes are often one of the first places where symptoms appear. Here are some key signs that may indicate the presence of a brain tumor:
- Blurred or Double Vision: Tumors located near the optic nerve or in areas of the brain that control eye movement can cause blurred or double vision.
- Optic Disc Swelling: As mentioned earlier, papilledema is a telltale sign of increased intracranial pressure, which can be caused by a brain tumor.
- Vision Loss: Sudden or gradual vision loss in one or both eyes can occur if the tumor affects the visual pathways in the brain.
- Abnormal Eye Movements: Tumors can disrupt the nerves that control eye movement, leading to jerky or uncoordinated eye movements.
It’s important to note that these symptoms are not exclusive to brain tumors and can be caused by other conditions, such as migraines, diabetes, or glaucoma. However, if these symptoms persist or worsen, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly.
Can an Eye Doctor Detect a Brain Tumor?
Yes, an eye doctor can play a pivotal role in detecting brain tumors, but their role is often limited to identifying warning signs rather than diagnosing the tumor itself. Eye doctors are trained to recognize abnormalities during routine exams, such as optic nerve swelling or vision disturbances, which may prompt them to refer patients to a neurologist for further evaluation.
Read also:Catriona Gray Boyfriend Now A Glimpse Into Her Love Life And Career
For example, if an eye doctor notices papilledema during a routine exam, they will likely recommend imaging tests like an MRI or CT scan to determine the cause. While the eye doctor cannot diagnose a brain tumor directly, their observations can lead to early detection, which is critical for successful treatment.
How Does Early Detection Impact Treatment?
Early detection of a brain tumor can significantly improve treatment outcomes. When tumors are identified early, they are often smaller and more localized, making them easier to treat with surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy. Additionally, early intervention can prevent further damage to the brain and eyes, preserving vision and overall quality of life.
What Are the Most Common Misconceptions?
One common misconception is that brain tumors are always accompanied by severe headaches or seizures. While these symptoms can occur, they are not always present, especially in the early stages. Another misconception is that only neurologists can detect brain tumors. In reality, eye doctors are often the first to notice warning signs during routine exams.
How Do Brain Tumors Affect Vision?
Brain tumors can impact vision in several ways, depending on their location and size. Tumors that press on the optic nerve or visual pathways in the brain can cause a range of vision problems, from mild blurriness to complete vision loss. Here’s a closer look at how brain tumors affect vision:
- Optic Nerve Compression: Tumors near the optic nerve can compress it, leading to vision loss or blind spots.
- Visual Field Defects: Tumors in the occipital lobe, the part of the brain responsible for processing visual information, can cause blind spots or tunnel vision.
- Double Vision: Tumors affecting the cranial nerves that control eye movement can result in double vision.
Understanding these effects can help patients recognize symptoms early and seek appropriate care.
What Should You Do If a Problem Is Suspected?
If you experience any vision changes or symptoms that could indicate a brain tumor, it’s important to act quickly. Start by scheduling an appointment with your eye doctor for a thorough examination. If the eye doctor identifies any abnormalities, they will likely refer you to a neurologist for further testing.
In the meantime, keep a detailed record of your symptoms, including when they started, how often they occur, and any factors that make them better or worse. This information can be invaluable for your healthcare providers as they work to determine the cause of your symptoms.
Why Are Regular Eye Exams Important for Brain Health?
Regular eye exams are not just about maintaining good vision; they are also an essential part of overall health maintenance. Eye doctors are often the first line of defense in detecting systemic conditions, including brain tumors, diabetes, and hypertension. By catching these conditions early, patients can receive timely treatment and improve their long-term outcomes.
For this reason, it’s recommended that adults have a comprehensive eye exam at least once every two years, or more frequently if they have risk factors such as a family history of eye or neurological conditions.
What Are the Limits of Eye Doctors in Brain Tumor Detection?
While eye doctors are skilled at identifying signs that may indicate a brain tumor, they are not equipped to diagnose or treat tumors themselves. Their role is to recognize abnormalities and refer patients to specialists for further evaluation. It’s also important to note that not all brain tumors present with visible signs in the eyes, so a normal eye exam does not rule out the possibility of a tumor.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can an Eye Doctor Detect a Brain Tumor During a Routine Exam?
Yes, an eye doctor can detect signs of a brain tumor during a routine exam, such as optic disc swelling or vision changes. However, further testing by a neurologist is required for a definitive diagnosis.
What Should I Do If My Eye Doctor Suspects a Brain Tumor?
If your eye doctor suspects a brain tumor, they will likely refer you to a neurologist for imaging tests like an MRI or CT scan to confirm the diagnosis.
Are Vision Problems Always a Sign of a Brain Tumor?
No, vision problems can be caused by a variety of conditions, such as migraines, diabetes, or glaucoma. However, persistent or unexplained symptoms should always be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Conclusion
While the idea of an eye doctor detecting a brain tumor might seem surprising, it’s a testament to the interconnectedness of our body systems. Regular eye exams are not just about maintaining good vision; they can also serve as a vital tool for early detection of serious health conditions. By staying informed and proactive about your health, you can ensure that any potential issues are addressed promptly and effectively.
For more information on brain tumors and their symptoms, visit the American Cancer Society.