Graves or Hashimoto's disease are two of the most common autoimmune thyroid disorders, each with distinct characteristics and effects on the body. These conditions can significantly impact a person’s quality of life if left untreated, but with proper management, individuals can lead healthy and fulfilling lives. While both diseases involve the thyroid gland, they differ in how they affect its function. Graves’ disease causes the thyroid to become overactive, leading to hyperthyroidism, whereas Hashimoto’s disease results in an underactive thyroid, known as hypothyroidism. Understanding the differences between these conditions is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment.
These disorders are more common than many people realize, affecting millions worldwide. Women are particularly at risk, with both conditions being more prevalent in females than males. The exact causes of Graves or Hashimoto's disease remain unclear, but researchers believe that a combination of genetic predisposition, environmental triggers, and immune system dysfunction plays a significant role. Early detection and treatment can prevent complications, such as heart problems, fertility issues, and even mental health challenges.
For those navigating the complexities of Graves or Hashimoto's disease, knowledge is power. By exploring the symptoms, diagnostic methods, and available treatments, individuals can take control of their health and work closely with healthcare providers to manage their condition. This article dives deep into the intricacies of these disorders, providing a comprehensive guide to help you understand and address the challenges they present.
Read also:Unpacking President Snows Character Traits A Deep Dive Into His Complex Personality
Table of Contents
- What Are Graves and Hashimoto’s Disease?
- What Causes These Autoimmune Disorders?
- How Do Symptoms Differ Between Graves and Hashimoto’s?
- Diagnosing Graves or Hashimoto’s Disease
- What Are the Treatment Options Available?
- Lifestyle Changes to Manage Thyroid Disorders
- Can Diet Help Alleviate Symptoms?
- Frequently Asked Questions About Graves or Hashimoto’s Disease
What Are Graves and Hashimoto’s Disease?
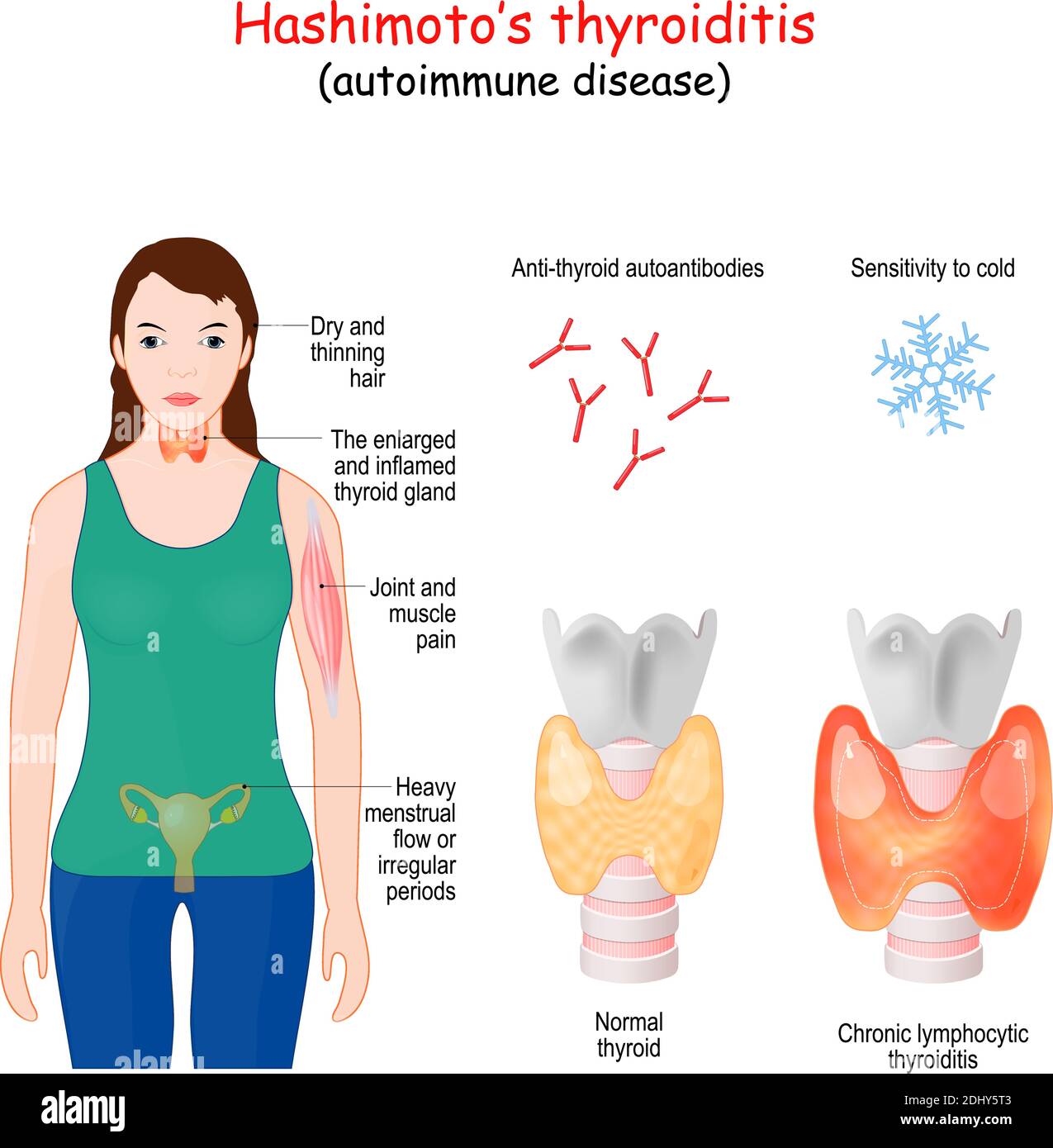
Graves’ disease and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis are autoimmune disorders that target the thyroid gland, a small butterfly-shaped organ located in the neck. While both conditions involve the immune system mistakenly attacking the thyroid, they lead to opposite effects on its function. Graves’ disease is characterized by an overproduction of thyroid hormones, resulting in hyperthyroidism. This excess hormone activity can cause symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, weight loss, anxiety, and bulging eyes. On the other hand, Hashimoto’s disease leads to the destruction of thyroid tissue, causing an underproduction of hormones and resulting in hypothyroidism. Symptoms of hypothyroidism include fatigue, weight gain, depression, and sensitivity to cold.
Understanding the underlying mechanisms of these diseases is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment. Graves’ disease is often associated with specific antibodies, such as thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins (TSIs), which bind to thyroid receptors and stimulate hormone production. In contrast, Hashimoto’s disease involves the production of antibodies that attack and damage thyroid cells, eventually impairing hormone synthesis. Both conditions can have a profound impact on an individual’s physical and emotional well-being, making it crucial to address them promptly.
While these disorders are distinct, they share some commonalities. Both are more prevalent in women and tend to run in families, suggesting a genetic component. Environmental factors, such as stress, infections, and exposure to certain chemicals, may also play a role in triggering these autoimmune responses. By recognizing the differences and similarities between Graves or Hashimoto's disease, individuals can better navigate their healthcare journey and seek appropriate treatment.
What Causes These Autoimmune Disorders?
The exact causes of Graves or Hashimoto's disease remain a subject of ongoing research, but experts believe that a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors contribute to their development. Autoimmune disorders occur when the body’s immune system mistakenly identifies its own cells as foreign invaders and launches an attack. In the case of Graves’ disease, the immune system produces antibodies that stimulate the thyroid gland to produce excessive amounts of hormones. Hashimoto’s disease, on the other hand, involves antibodies that destroy thyroid tissue, leading to hormone deficiency.
Genetic Predisposition: Are You at Risk?
Family history plays a significant role in the development of autoimmune thyroid disorders. If a close relative has Graves or Hashimoto's disease, your risk of developing the condition increases. Researchers have identified specific genes that may predispose individuals to these disorders, although not everyone with these genetic markers will develop symptoms. Understanding your family history can help you take proactive steps, such as regular thyroid function tests, to monitor your health.
Environmental Triggers: What Role Do They Play?
Environmental factors, such as stress, infections, and exposure to toxins, can trigger or exacerbate autoimmune responses. For instance, viral infections like Epstein-Barr virus have been linked to the onset of Hashimoto’s disease. Similarly, high levels of physical or emotional stress may contribute to the development of Graves’ disease. Lifestyle factors, including smoking and nutrient deficiencies, can also influence the immune system and increase the risk of these conditions.
Read also:Desire Movie Com 2024 Hindi Dubbed A Complete Guide To The Most Anticipated Release
How Do Symptoms Differ Between Graves and Hashimoto’s?
Recognizing the symptoms of Graves or Hashimoto's disease is essential for early diagnosis and treatment. While both conditions affect the thyroid, their symptoms are vastly different due to the opposing effects on hormone production. Graves’ disease, with its hallmark hyperthyroidism, often presents with symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, anxiety, tremors, and unintentional weight loss. Patients may also experience bulging eyes (Graves’ ophthalmopathy) and thickened skin on the shins. These symptoms result from the overstimulation of the body’s metabolism due to excessive thyroid hormone levels.
Common Symptoms of Graves’ Disease
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat (palpitations)
- Increased sweating and heat intolerance
- Weight loss despite increased appetite
- Nervousness, irritability, and anxiety
- Difficulty sleeping (insomnia)
Recognizing Hashimoto’s Disease: What to Look For
In contrast, Hashimoto’s disease leads to hypothyroidism, which slows down the body’s metabolism. Common symptoms include fatigue, weight gain, depression, and sensitivity to cold. Patients may also notice dry skin, hair loss, and muscle weakness. As the condition progresses, it can lead to complications such as goiter (enlarged thyroid) and fertility issues. Understanding these differences can help individuals seek appropriate medical attention and avoid misdiagnosis.
Diagnosing Graves or Hashimoto’s Disease
Diagnosing Graves or Hashimoto's disease requires a combination of clinical evaluation, blood tests, and imaging studies. The first step typically involves a thorough medical history and physical examination to identify symptoms and risk factors. Blood tests are then used to measure thyroid hormone levels, including thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), free T3, and free T4. In Graves’ disease, TSH levels are usually low, while T3 and T4 levels are elevated. In Hashimoto’s disease, the opposite occurs, with high TSH levels and low T3 and T4 levels.
Additional Diagnostic Tools: What Tests Are Used?
Beyond hormone tests, specific antibody tests can help confirm the diagnosis. For Graves’ disease, the presence of thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins (TSIs) is a key indicator. In Hashimoto’s disease, anti-thyroid peroxidase (TPO) and anti-thyroglobulin antibodies are commonly detected. Imaging studies, such as ultrasound or radioactive iodine uptake tests, may also be used to assess the size and function of the thyroid gland. Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective management of these conditions.
What Are the Treatment Options Available?
Treatment for Graves or Hashimoto's disease varies depending on the specific condition and its severity. For Graves’ disease, options include antithyroid medications like methimazole, radioactive iodine therapy to reduce thyroid activity, or surgery to remove part or all of the thyroid gland. Beta-blockers may also be prescribed to manage symptoms such as rapid heartbeat and tremors. In contrast, Hashimoto’s disease is typically managed with synthetic thyroid hormone replacement therapy, such as levothyroxine, to restore normal hormone levels and alleviate symptoms.
Lifestyle Modifications: Can They Complement Treatment?
In addition to medical interventions, lifestyle changes can play a supportive role in managing these conditions. Stress reduction techniques, regular exercise, and a balanced diet can help improve overall well-being and minimize symptom flare-ups. Consulting with a healthcare provider is essential to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses individual needs and goals.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Thyroid Disorders
Adopting healthy lifestyle habits can significantly improve the management of Graves or Hashimoto's disease. Stress management techniques, such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises, can help regulate the immune system and reduce the risk of symptom exacerbation. Regular physical activity not only boosts energy levels but also supports mental health, which is particularly important for individuals dealing with chronic conditions.
Stress Management: Why Is It Important?
Chronic stress can worsen autoimmune responses and trigger flare-ups in both Graves’ and Hashimoto’s disease. Incorporating relaxation techniques into your daily routine can help maintain a balanced immune system and improve overall quality of life. Additionally, ensuring adequate sleep and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule can further support thyroid health.
Can Diet Help Alleviate Symptoms?
Diet plays a crucial role in managing Graves or Hashimoto's disease. Certain nutrients, such as selenium, zinc, and iodine, are essential for thyroid function, while others, like gluten, may exacerbate symptoms in some individuals. A diet rich in whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, can provide the necessary nutrients to support thyroid health. Avoiding processed foods and excessive sugar intake is also beneficial for overall well-being.
Nutrient-Rich Foods for Thyroid Health
- Brazil nuts (high in selenium)
- Fatty fish (rich in omega-3 fatty acids)
- Leafy greens (packed with antioxidants)
- Probiotic-rich foods like yogurt and kefir
Frequently Asked Questions About Graves or Hashimoto’s Disease
1. Can Graves or Hashimoto’s Disease Be Cured?
While there is no permanent cure for Graves or Hashimoto's disease, both conditions can be effectively managed with appropriate treatment. Consistent monitoring and adherence to a treatment plan can help individuals lead healthy and fulfilling lives.
2. Are These Conditions Hereditary?
Yes, both Graves’ and Hashimoto’s disease have a genetic component. If a family member has one of these conditions, your risk of developing it increases. However, environmental factors also play a significant role.
3. How Can I Support a Loved One with These Conditions?
Offering emotional support, encouraging healthy lifestyle choices, and helping them stay consistent with their treatment plan can make a significant difference. Educating yourself about the condition can also foster understanding and empathy.
Conclusion
Graves or Hashimoto's disease are complex autoimmune disorders that require careful management and a proactive approach to health. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take control of their well-being and work closely with healthcare providers to achieve optimal outcomes. Whether through medical interventions, lifestyle changes, or dietary adjustments, there are numerous ways to manage these conditions effectively. For more information, you can explore resources such as the American Thyroid Association.